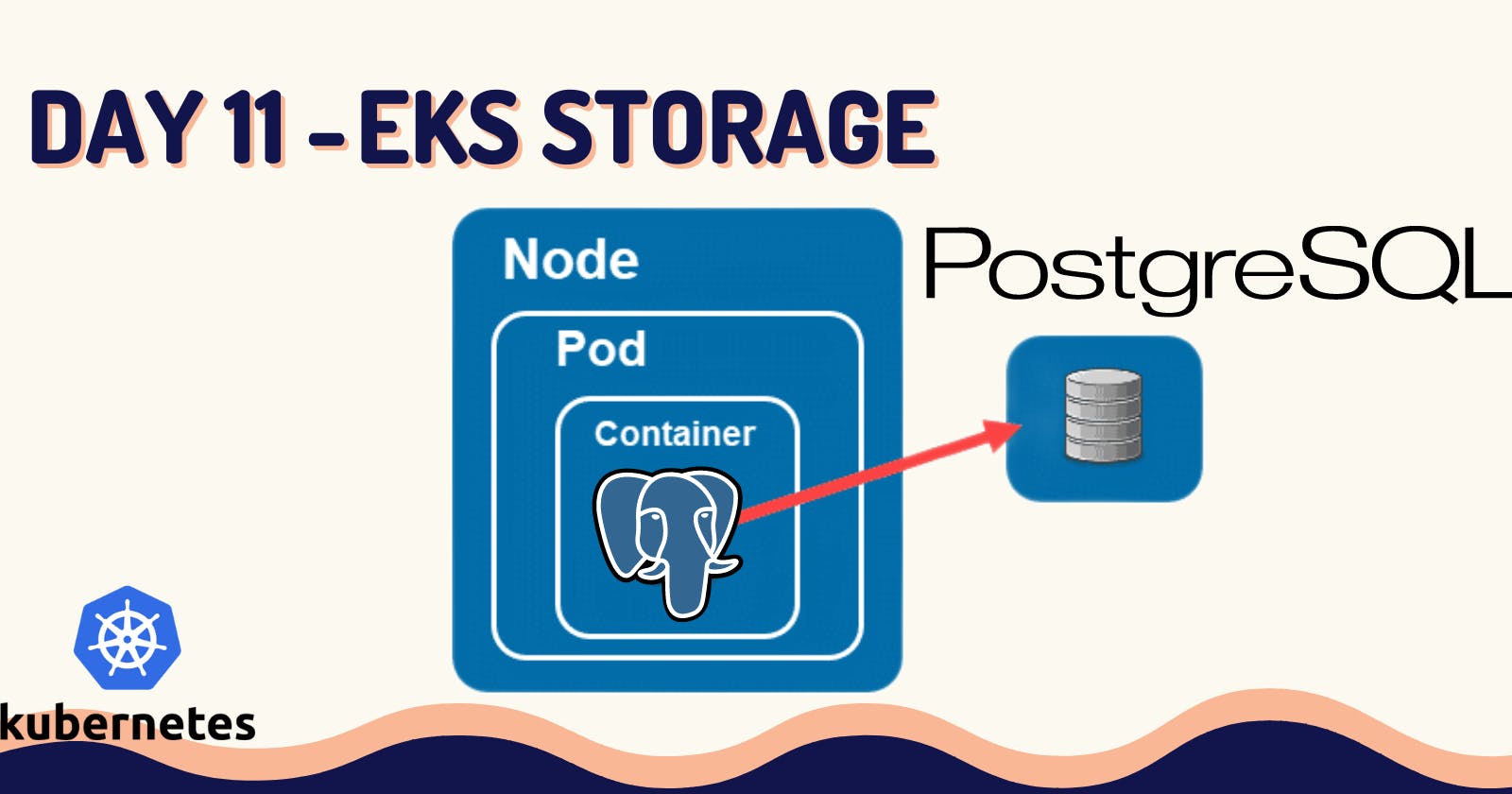
(1) Introduction:
- We are going to create a Postgres database with persistence storage using AWS EBS Volumes.
| Kubernetes Object | YAML File |
| Storage Class | 01-storage-class.yml |
| Persistent Volume Claim | 02-pvc.yml |
| Config Map | 03-create-db-configmap.yml |
| Deployment, Environment Variables, Volumes, VolumeMounts | 04-pg-deployment.yml |
| ClusterIP Service | 05-pg-service.yml |
(2) Create the following Kubernetes manifests.
(i) Create a Storage Class manifest.
(ii) Create Persistent Volume Claims manifest.
# Create Storage Class & PVC
kubectl apply -f kube-configs/
# List Storage Classes
kubectl get sc
# List PVC
kubectl get pvc
# List PV
kubectl get pv
(iii) Create ConfigMap manifest
- We are going to create a
railsv1database during thepostgrespod creation. we will use it when we deploy Application Microservice.
(iv) Create Postgres Deployment.
Environment Variables
Volumes
Volume Mounts
(v) Create Postgres ClusterIP Service manifest.
- At any point in time, we are going to have only one
postgrespod in this design soClusterIP: Nonewill use thePod IP Addressinstead of creating or allocating a separate IP forPostgres Cluster IP service.
(3) Create Postgres Database with all the above Kube-configs.
# Create Postgres Database
kubectl apply -f kube-manifests/
# List Storage Classes
kubectl get sc
# List PVC
kubectl get pvc
# List PV
kubectl get pv
# List pods
kubectl get pods
# List pods based on label name
kubectl get pods -l app=postgres
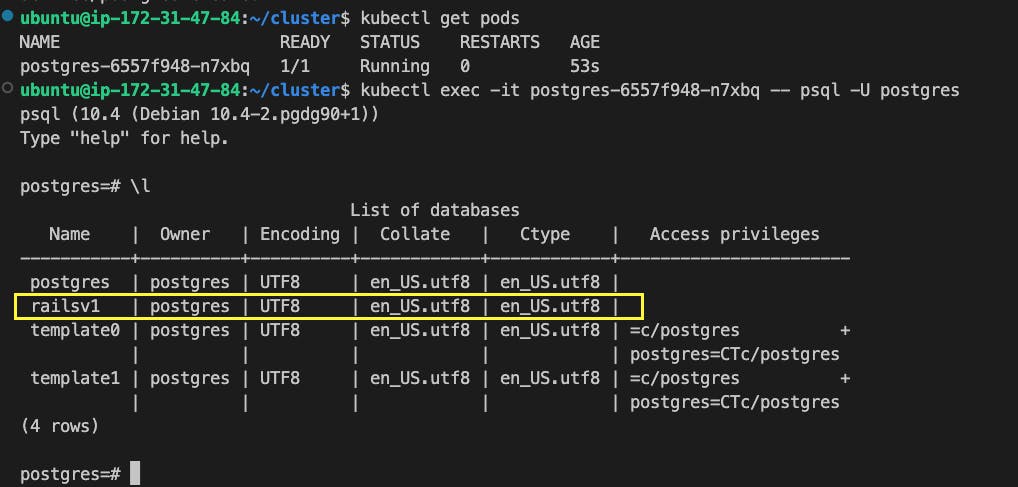
(4) Connect to Postgres Database.
kubectl exec -it pod-name -- psql -U postgres
(5) Verify 'railsv1' DB is created.
Made with ♥ by Pratikkumar Panchal